Microstructure evolution mechanism of single and multi-pass in laser cladding based on heat accumulation effect for invar alloy
Zhu S, Yu C, Chang Z, et al. Microstructure evolution mechanism of single and multi-pass in laser cladding based on heat accumulation effect for invar alloy[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2021: 1-17.

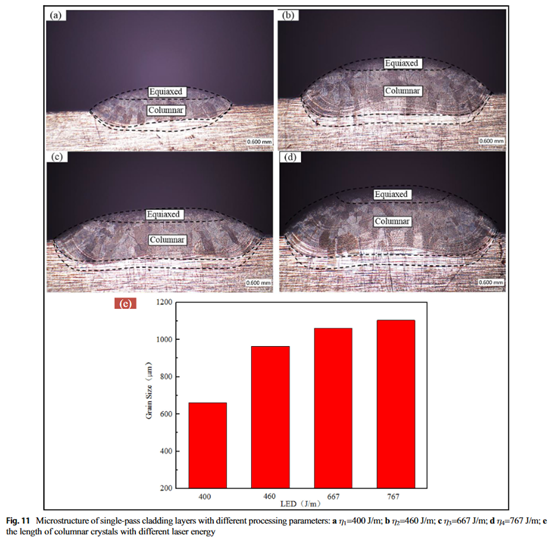
This work explores how the process parameters in laser cladding affect the evolution of the microstructure of the single-pass and multi-pass cladding layers of Invar alloys. The research examined the cladding layers from three aspects: (1) the transformation of grain size, heat-affected zone (HAZ) width, ratio of the columnar crystal to the equiaxed crystal, and change of Fe content of the cladding layer; (2) the effects of heat accumulation on grain size, HAZ width, and remelting zone; and (3) the hardness distribution of single-pass and multi-pass cladding layers. The investigation has the following four findings: (1) the cladding layer is composed of equiaxed crystals at the top and columnar crystals at the bottom of the cladding layer; (2) the processing parameters have significant effects on the width of the HAZ, proportion between the columnar and equiaxed crystals, and the change of Fe content of the cladding layer; (3) the gradual accumulation of heat causes the increase in HAZ width, the grain size, and the area of the remelting zone; and (4) the hardness progressively reduces from the top to the bottom along the direction of the centerline of the cladding layer.